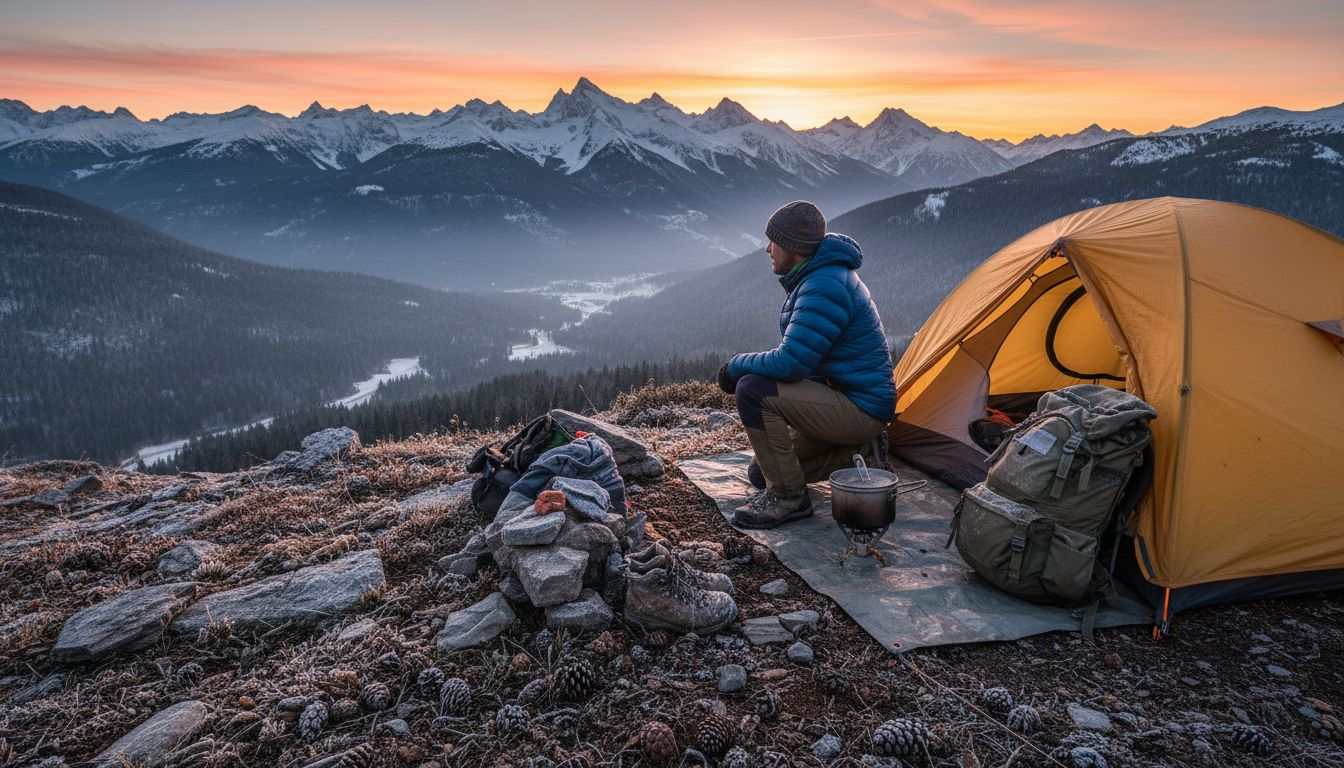

More than 60 percent of American campers are interested in exploring new outdoor challenges, with high-altitude adventures topping the list. The thrill of climbing above the tree line brings fresh air, breathtaking views, and the hidden dangers of reduced oxygen and extreme weather. Understanding the real risks and common myths of high-altitude camping can help both beginners and seasoned American explorers stay safe and get the most out of every elevated journey.
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Understanding High-Altitude Camping | High-altitude camping begins at around 8,000 feet and requires specific skills and equipment for safe exploration. It is accessible to reasonably fit adventurers, not just professionals. |
| Myth Busting | Many misconceptions suggest high-altitude camping is only for experts or requires expensive gear. In reality, proper preparation, acclimatization, and basic gear understanding make it attainable for many. |
| Critical Gear Essentials | Successful high-altitude camping relies on specialized gear designed for extreme conditions, prioritizing weight, durability, and thermal performance. Essential items include navigation tools, emergency shelters, and high-performance clothing. |
| Health and Safety Precautions | Awareness of altitude sickness and weather unpredictability is crucial. Gradual acclimatization, proper hydration, and comprehensive emergency plans can significantly enhance safety and enjoyment in high-altitude environments. |
Defining High-Altitude Camping and Common Myths
High-altitude camping represents a unique outdoor adventure that challenges campers to explore terrain above typical elevation ranges. Unlike standard camping experiences, high-altitude environments demand specialized skills, equipment, and physiological adaptations. These locations typically start around 8,000 feet above sea level, where atmospheric oxygen levels begin to noticeably decrease.
Contrary to popular misconceptions, high-altitude camping isn't just for extreme mountaineers. Weekend adventurers can safely enjoy these environments by understanding key principles. Altitude tents simulate higher elevation conditions and help campers gradually acclimate to reduced oxygen environments. This technique allows outdoor enthusiasts to prepare their bodies for challenging terrain without immediate exposure to extreme conditions.
Several persistent myths surround high-altitude camping that discourage potential explorers. Some believe only professional climbers can successfully camp at elevation, while others assume specialized gear is prohibitively expensive. In reality, careful preparation, gradual acclimatization, and basic understanding of physiological responses can make high-altitude camping accessible to most reasonably fit outdoor enthusiasts. Understanding proper hydration, recognizing altitude sickness symptoms, and selecting appropriate gear are critical skills for safe and enjoyable high-elevation experiences.
Pro Camping Safety Tip: Gradually increase your elevation exposure during multi-day trips, drink plenty of water, and monitor your body's response to prevent altitude-related health risks. Always carry emergency communication devices and inform someone about your planned route and expected return time.
Types of Sites and Typical Destinations
High-altitude camping destinations range from rugged mountain ranges to remote alpine landscapes, offering adventurers diverse environments that challenge and inspire. The Rocky Mountains, Sierra Nevada, Andes, and Himalayan ranges represent premier locations for experienced high-altitude campers seeking breathtaking terrain and extreme elevation experiences. These regions provide unique opportunities for portaledge camping, where climbers can suspend their sleeping platforms on sheer rock faces, creating an extraordinary camping experience that defies traditional ground-based setups.
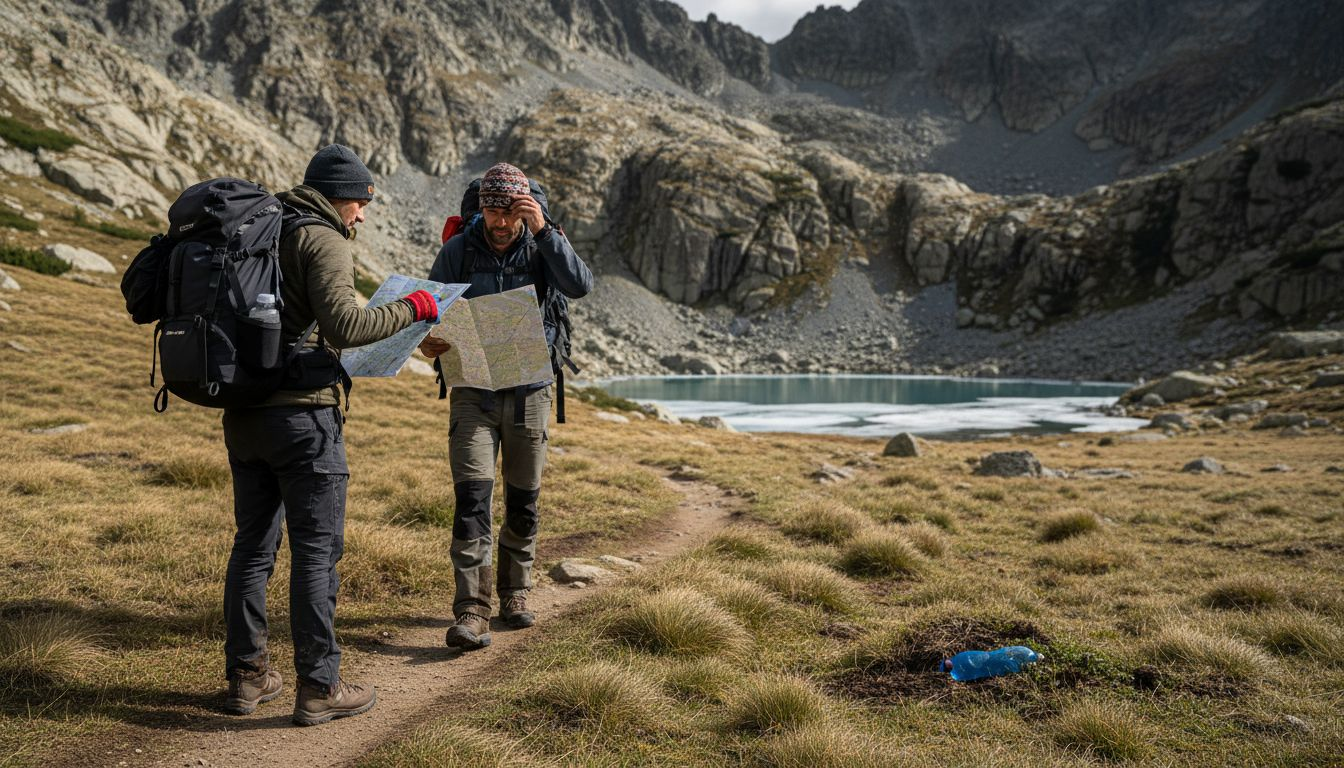 Popular high-altitude camping destinations typically feature elevations between 8,000 and 14,000 feet, with specific regions offering distinct challenges and scenic views. The Colorado Rockies, for instance, provide numerous alpine lakes and mountain passes perfect for adventurers. National Parks like Rocky Mountain, Yosemite, and Grand Teton offer designated high-elevation camping zones with carefully managed access points. Some advanced camping locations include Mount Whitney in California, Mount Elbert in Colorado, and select regions in Alaska that demand sophisticated mountaineering and camping skills.
Popular high-altitude camping destinations typically feature elevations between 8,000 and 14,000 feet, with specific regions offering distinct challenges and scenic views. The Colorado Rockies, for instance, provide numerous alpine lakes and mountain passes perfect for adventurers. National Parks like Rocky Mountain, Yosemite, and Grand Teton offer designated high-elevation camping zones with carefully managed access points. Some advanced camping locations include Mount Whitney in California, Mount Elbert in Colorado, and select regions in Alaska that demand sophisticated mountaineering and camping skills.
Unique camping techniques have emerged to accommodate challenging high-altitude terrains. Hammock camping provides lightweight alternative sleeping arrangements that work exceptionally well in mountainous environments. These suspended sleeping systems allow campers to avoid uneven ground, rocky surfaces, and potential water accumulation while maintaining a compact and portable setup. Advanced campers often combine multiple techniques, using specialized lightweight gear designed for extreme elevation conditions that minimize pack weight while maximizing survival capabilities.
Pro Campsite Selection Tip: Research specific high-altitude campground regulations, obtain necessary permits, and verify current weather conditions before planning your expedition. Always check elevation-specific guidelines and potential seasonal access restrictions for your chosen mountain destination.
Here's a comparison of popular high-altitude camping destinations and what makes each unique:
| Destination Region | Typical Elevation Range | Signature Features | Experience Level Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado Rockies | 8,000–14,000 ft | Alpine lakes, varied weather | Beginner to Advanced |
| Sierra Nevada | 7,000–14,500 ft | Steep granite peaks, clear skies | Intermediate to Advanced |
| Andes | 9,000–20,000 ft | High passes, remote landscapes | Advanced |
| Himalayas | 10,000–18,000+ ft | Glaciers, extreme altitude | Expert |
| Alaska (select areas) | 10,000–20,000+ ft | Glacial terrain, severe cold | Advanced to Expert |
Key Gear and Survival Essentials Needed
Successful high-altitude camping demands precise gear selection that goes beyond standard outdoor equipment. The Ten Essentials represent a critical foundation for mountain survival, providing campers with a comprehensive checklist of survival necessities. These essential items include navigation tools, emergency shelter, first aid supplies, fire-starting equipment, extra food and water, and protective clothing designed to withstand extreme environmental conditions.
Specialized high-altitude gear requires careful consideration of weight, durability, and thermal performance. Comprehensive expedition gear checklists recommend specific items like waterproof trekking boots, layered clothing systems, and technical climbing equipment, ensuring adventurers can manage unpredictable mountain environments. Critical gear categories include insulated outerwear, moisture-wicking base layers, high-performance sleeping bags rated for extreme temperatures, and technical accessories like crampons, ice axes, and climbing harnesses that enable safe movement across challenging terrain.
Beyond individual equipment, high-altitude camping requires advanced preparation and understanding of gear functionality. Lightweight, multi-purpose tools become essential, with compact designs that maximize utility while minimizing pack weight. Emergency communication devices, portable water filtration systems, high-calorie nutrition packs, and advanced navigation technologies represent crucial investments for mountain adventurers seeking to balance safety and exploration.
Pro Gear Preparation Tip: Always test and familiarize yourself with specialized high-altitude equipment before your expedition, ensuring each piece functions correctly and fits comfortably in extreme conditions. Pack redundant critical items like fire-starting tools and emergency communication devices to maximize your survival preparedness.
Altitude Sickness, Weather, and Safety Risks
High-altitude camping presents significant physiological challenges that demand comprehensive understanding and proactive management. Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS) represents the primary health risk for adventurers ascending rapidly to elevations above 8,000 feet, with symptoms including headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and potential respiratory complications. High-altitude environments dramatically accelerate dehydration processes, where cold air reduces natural thirst responses while increasing fluid loss through rapid breathing and dry atmospheric conditions.
Weather conditions in high-altitude environments create unpredictable and potentially life-threatening scenarios. Temperature fluctuations can range dramatically, with daytime temperatures potentially dropping 30 to 40 degrees within hours, creating serious risks of hypothermia and exposure. Wind chill factors become exponentially more dangerous at higher elevations, where reduced atmospheric pressure diminishes the body's ability to regulate temperature. Mountaineering experts recommend a layered clothing approach that allows rapid adaptation to changing environmental conditions, with moisture-wicking base layers, insulating mid-layers, and waterproof outer shells.
Risk mitigation in high-altitude camping requires systematic preparation and continuous situational awareness. Advanced campers utilize multiple strategies including gradual elevation acclimatization, maintaining precise hydration protocols, monitoring individual and group health indicators, and carrying comprehensive emergency communication and first aid equipment. Understanding individual physiological limitations, recognizing early warning signs of altitude-related medical complications, and maintaining flexible expedition plans become critical survival strategies in challenging mountain environments.
Pro Safety Strategy: Develop a comprehensive emergency communication plan that includes satellite communication devices, detailed location sharing with support teams, and predetermined evacuation protocols before entering high-altitude terrain. Always travel with experienced companions who understand mountain rescue techniques and can provide immediate medical support if required.
Here is a summary of key risk factors at high altitude and effective prevention strategies:
| Risk Factor | Description | Prevention Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Mountain Sickness | Headache, fatigue at elevation | Slow ascent, acclimatization |
| Severe Weather Fluctuations | Drastic temperature swings, sudden storms | Layered clothing, weather check |
| Dehydration | Increased fluid loss, reduced thirst | Scheduled water intake |
| Navigation Challenges | Poor visibility, complex terrain | GPS devices, updated maps |
Tips for Beginners and Common Mistakes
High-altitude camping demands a strategic approach that distinguishes successful adventurers from novice travelers. First-time mountain campers often make critical errors by underestimating the complexity of alpine environments, rushing their preparations, and failing to understand the unique challenges presented by elevation and terrain. Essential gear preparation includes carefully selecting multi-purpose equipment that covers emergency communication, navigation, and survival needs, ensuring campers remain adaptable in unpredictable mountain conditions.
Common mistakes among beginners include inadequate physical conditioning, improper acclimatization techniques, and overpacking unnecessary equipment that increases physical strain. Novice campers frequently carry excessive weight, compromise their mobility, and underestimate the importance of lightweight, versatile gear that supports mobility and survival. Experienced mountaineers recommend a minimalist approach focusing on high-performance, compact equipment that addresses multiple survival requirements while maintaining flexibility and reducing physical exhaustion.
Successful high-altitude camping requires comprehensive preparation that extends beyond physical equipment. Mental preparation, understanding personal physiological limitations, and developing robust risk management strategies become equally important. Beginners should prioritize gradual skill development, seek mentorship from experienced alpine travelers, participate in preparatory training courses, and incrementally challenge themselves by selecting progressively more difficult terrain and elevation ranges. Developing a systematic approach to mountain exploration allows travelers to build confidence, enhance technical skills, and minimize potential safety risks.
Pro Learning Strategy: Start with guided mountain experiences, take professional wilderness survival courses, and always communicate your detailed expedition plan with trusted contacts who can monitor your progress and provide emergency support if needed.
Gear Up for High-Altitude Camping Success with Life Camp Adventure
High-altitude camping demands specialized knowledge and reliable gear to overcome challenges like acute mountain sickness, unpredictable weather, and rugged terrain. If you are preparing to take on these elevated adventures, you need equipment that supports gradual acclimatization, layered protection, and lightweight portability so you can focus on exploring safely and confidently. Life Camp Adventure understands these unique needs and offers a curated selection of camping essentials and survival gear designed just for high-altitude conditions.
Take the next step toward mastering your mountain experience by browsing our high-quality camping equipment built to perform in extreme environments. Equip yourself with trusted gear that enhances hydration management, safeguards against severe weather, and simplifies campsite setup. Don’t let altitude-related risks hold you back. Visit Life Camp Adventure today to discover durable, comfortable solutions that prepare you for the heights. Your ultimate outdoor adventure starts here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is high-altitude camping?
High-altitude camping refers to outdoor camping experiences that take place at elevations typically above 8,000 feet, where oxygen levels decrease and campers face unique environmental challenges.
What are the risks associated with high-altitude camping?
The primary risks include Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS), severe weather fluctuations, dehydration, and navigation challenges due to complex terrains and poor visibility.
How can I prepare for high-altitude camping?
Preparation involves gradual acclimatization to higher elevations, selecting appropriate gear, maintaining hydration, and understanding weather conditions. Developing a systematic approach to mountain exploration is essential.
What essential gear do I need for high-altitude camping?
Essential gear includes navigation tools, emergency shelter, first aid supplies, fire-starting equipment, moisture-wicking clothing layers, high-performance sleeping bags, and specialized climbing equipment.
